1
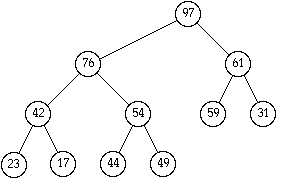
The following array of current size 11 represents a heap structure:
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 |
| 97 | 76 | 61 | 42 | 54 | 59 | 31 | 23 | 17 | 44 | 49 |
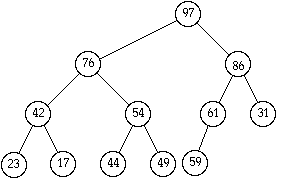
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 |
| 97 | 76 | 61 | 42 | 54 | 59 | 31 | 23 | 17 | 44 | 49 | 86 |
| 97 | 76 | 86 | 42 | 54 | 61 | 31 | 23 | 17 | 44 | 49 | 59 |
b.
(10 points)
Start again with the original heap of 11 elements. Show the result of each pass of
HEAPSORT. Note: After one pass 97 is in position 11 and the values in positions
1 .. 10 again form a heap.
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 |
| 97 | 76 | 61 | 42 | 54 | 59 | 31 | 23 | 17 | 44 | 49 |
| 76 | 54 | 61 | 42 | 49 | 59 | 31 | 23 | 17 | 44 | 97 |
| 61 | 54 | 59 | 42 | 49 | 44 | 31 | 23 | 17 | 76 | 97 |
| 59 | 54 | 44 | 42 | 49 | 17 | 31 | 23 | 61 | 76 | 97 |
| 54 | 49 | 44 | 42 | 23 | 17 | 31 | 59 | 61 | 76 | 97 |
| 49 | 42 | 44 | 31 | 23 | 17 | 54 | 59 | 61 | 76 | 97 |
| 44 | 42 | 17 | 31 | 23 | 49 | 54 | 59 | 61 | 76 | 97 |
| 42 | 31 | 17 | 23 | 44 | 49 | 54 | 59 | 61 | 76 | 97 |
| 31 | 23 | 17 | 42 | 44 | 49 | 54 | 59 | 61 | 76 | 97 |
| 23 | 17 | 31 | 42 | 44 | 49 | 54 | 59 | 61 | 76 | 97 |
| 17 | 23 | 31 | 42 | 44 | 49 | 54 | 59 | 61 | 76 | 97 |
2. (5 points) Write a C++ function that takes as input a pointer to the root of a binary tree, and prints the node values of the tree in level order. Assume you have available a Queue Class, to build a queue of node pointers, with the following public member functions:
// default constructor (makes the empty queue) Queue (); // destructor ~Queue(); // conditionals: empty? full? - DonŐt worry about full. bool IsEmpty (); // add new item to the queue Queue& Enqueue (Node* data); // remove item from the queue Node* Dequeue (); };void levelOrder(Node* t){ Queue Q; if (t) Q.Enqueue(t); while (!Q.IsEmpty()){ Node* p = Q.Dequeue(); cout << P->data << endl; if (p->left) Q.Enqueue(p-left); if (p->right) Q.Enqueue(p->right); } }
3. (5 points)Write a recursive function
int PrintRange(Node* root, int low, int high);that given a Binary Search Tree and low and high values, prints all records (data values) that fall between the two values. For full credit, the function PrintRange should visit as few nodes as possible.
int PrintRange(Node* root, int low, int high){
// This will print the records in order
if (root){
datatype d = root->data;
if ((low < d) && (root->left)) PrintRange(root->left, low, high);
if ((low <= d) && (d <= high)) cout << root->data << endl;
if ((d < high) && (root->right)) PrintRange(root->right, low, high);
}
}
Last Updated: May 26, 1997 9:38 pm by