problems from Astrachan:
12:13 Write a function Reverse( ) that reverses the order of the nodes in a linked list. Reverse the list by changing pointers, not by swapping info fields.
void Reverse(Node * & list) // precondition: list = (a b c . . . d) // postcondition: list = (d . . . c b a), list reversedHere are two solutions. The first is iterative, the second recursive, but not pretty. A better solution would return Node* instead of void.
void Reverse(Node* &list){
if (list) // if list has 0 or 1 element, don't do anything
if ((list->next)){
// list has more than one element
Node* p = list->next;
list->next = NULL; // this will end the list
Node* q;
while ((p->next)){
q = p->next;
p->next = list;
list = p;
p = q;
}
p->next = list;
list = p;
}
}
void RecReverse(Node* &list, Node* &tail){
if (!list) tail = NULL; // empty list
else
if (!(list->next)){ // list has one element
tail = list;
}
else{
cout << "list-> " << list->data << endl;
Node* Rlist = list->next;
RecReverse(Rlist, tail); // reverse the rest of the list
list->next = NULL; // prepare first node to be end of list
tail->next = list; // put first node at end of reversed list
tail = list; // set tail to end of list
list = Rlist;
}
}
12:14 Write a function that doubles a linked list by duplicating each node, i.e. the list (a b c d) is changed into (a a b b c c d d). Use the header below where list is NOT passed by reference.
void DoubleList(Node * list)
// precondition: if list = (a b c d)
// postcondition: then list = (a a b b c c d d)
Node* DoubleList(Node* list){
Node* ptr = list;
Node* extra = NULL;
while (ptr){
extra = new Node; // create space for the new node
extra->data = ptr->data; // copy the data from original node
// insert extra node after original node
extra->next = ptr->next;
ptr->next = extra;
// advance ptr to next original node
ptr = extra->next;
}
}
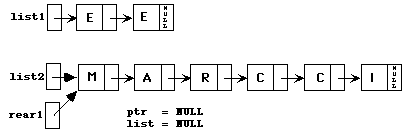
Problem 3
Original list for all three parts of the problem:

3a) The main loop in the code is:
while (rear1 != NULL) {
if (rear2 != NULL) {
rear1->next = rear2->next;
//rear1->next now points to node after rear2->
rear1 = rear2->next;
//rear1 now points to node after rear2->
}
else {
rear1->next = NULL; // the list is terminated by NULL
rear1 = NULL; // rear1 no longer points to the list
}
// the rest is as above with rear1 and rear2 reversed
if (rear1 != NULL) {
rear2->next = rear1->next;
rear2 = rear1->next;
}
else {
rear2->next = NULL;
rear2 = NULL;
}
}// rear1 and rear2 leap frog over each other, picking up alternate nodes
// of the original list.
rear1 = rear2 = NULL 
3b)
while (rear1 != NULL) {
if (rear1->data == 'E')
break;
else
rear1 = rear1->next;
}
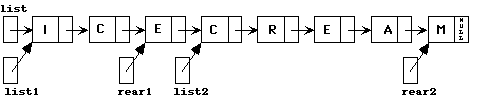
3c) Notice that in parts a) and b), the pointer list never changes. In this part, moves along the list until it becomes NULL. list1 collects all the nodes with character 'E' while list2 collects all the other nodes. rear1 never was used after it was set to list.

Last Updated: April 6, 1997 11:48 pm by