Problems
Problem 1 (25 points)
Courtesy James Allan
The purpose of this exercise is to gain some "hands-on" experience in the process of evaluating information retrieval systems. Run the following two queries on Google (http://google.com and on Bing (http://bing.com) (do not run the explanation; just run the query). You will judge 10 documents for relevance to the query. The explanation will help you decide whether or not something is relevant.- gardening wet soil conditions
What special considerations must be made when planting a garden in very wet soil conditions? Are there plants that will not work and/or that will work particularly well? Are there any special techniques that will help reduce the amount of moisture? Only pages that deal with gardening are relevant. - oil vs. propane furnace
Looking for pages that list the trade-offs for using a propane furnace rather than a fuel oil furnace. The pages should provide comparison and are only relevant if they talk about both. They can talk about other types of heating (e.g., electric), provided they talk about oil and propane. Propane is also called LP or LPG (liquid propane [gas]).
When judging pages for relevance, please note the following:
- A page is relevant if it is on the appropriate topic. It is not relevant only because it has a link to a page that has relevant content.
- Google indents some of the items on its ranked list to indicate that they come from the same domain (roughly) as the preceding entry. Include those entries. There should always be 10 entries per page.
- If a page is not found when you follow it, use the cached version. If there is no cached version, make your judgment from the title and snippet. If you cannot make a call with that information, mark it as non-relevant.
- 0 to 6 - do the first page (results 1-10)
- 7 to 9 - do the second page (results 11-20)
Use the following format (one result per line)
G-or-B query-number doc's-rank R-or-N doc's-title
G-or-B query-number doc's-rank R-or-N doc's-title
. . . . . .
where G-or-B indicates whether you ran this on Google or Bing, query-number is 1 or 2 from above, doc's-rank is the number from 1 to 20 (or more, if appropriate) of this document's rank, R-or-N is R if the page is relevant and N otherwise, and doc's-title is the title of the document (to help us verify that results make sense). Since you are judging 10 pages from each of two queries on each of two search engines, the file you submit should have 40 lines.
Problem 2 (25 points)
CourtesyJames Allan
-
The following list of R's and N's represents relevant (R) and non-relevant (N) documents in a ranked list of 50 documents. The top of the ranked list is on the left of the list, so that represents the most highly weighted document, the one that the system believes is most likely to be relevant. The list runs across the page to the right. This list shows 10 relevant documents. Assume that there are only 10 relevant and 40 non-relevat documents in the collection.
RRNRNRNNNN RNNNRNNNNR RNNNNNNNRN NNNNNNNNNN RNNNNNNNNN
Based on that list, calculate the following measures:
- Average precision
- Interpolated precision at 50% recall
- Interpolated precision at 33% recall
- R-precision
- Now, imagine another system retrieves the following ranked list for the same query.
RNNRNNNRNN NNNRNNNNNN NRNNNNNNRN NNRNNNNRNN NNNNRNNNNR
Repeat parts (A.1), (A.2), (A.3), and (A.4) for the above ranked list. Compare the two ranked lists on the basis of these four metrics that you have computed--i.e., if you were given only these four numbers (Mean Average Precision, Precision at 50% recall, Precision at 33% recall, and R-precision) what can you determine about the relative performance of the two systems in general.
- Plot a recall/precision graph for the above two systems. Generate both an uninterpolated and an interpolated graph (probably as two graphs to make the four plots easier to see). What do the graphs tell you about the system in A and the one in B?
- Plot ROC curves for the above two systems.
Problem 3 (25 points)
Define 'perfect-retrieval' as the list of ranked documents where (a) all the relevant documents are retrieved, and (b) every relevant document is ranked higher than any non-relevant one.
- Prove that at a list demonstrates perfect-retrieval if and only if there exists a cutoff=c such that the list has PREC(c)=1 and RECALL(c)=1
-
Consider a particular cutoff c=10
- Give example of a list that has PREC(10)=1 and RECALL(10)<1
- Give example of a list that has PREC(10)<1 and RECALL(10)=1
- Prove that a list demonstrates perfect-retrieval if and only if R_PREC=1
- Prove that a list demonstrates perfect-retrieval if and only if AveragePrecision=1
Consider a typical precision-recall curve starting at A (RECALL=0,PREC=1) and ending at B(RECALL=1,PREC=0)as shown in the plot (1) below.
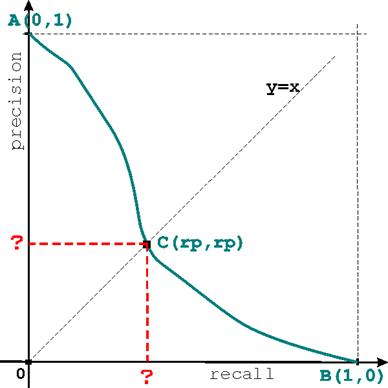
- Every point on the precision-recall curve corresponds to a particular rank (or cutoff). Intersect the curve with the main diagonal given by the equation y=xat point C (rp,rp). If the query in question has R relevant documents, at what rank does this intersection point corresponds to?
- As a consequence of the above, the quantity rp represents a standard retrieval metric. Explain which one and why.
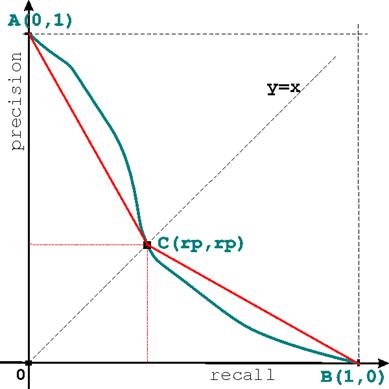
- As shown in plot (2), we now add the segments [AC] and [CB]. We are interested in the area under the blue precision-recall curve and we can approximate it by the area under the red lines ACB. Compute this approximation area as a function of rp.
- Explain how the average precision and R-precision measures are thus related.
Problem 5 - Extra Credit (15 points)
In this problem you are asked to implement Average Precision. The input to your program will be two files, (a) the ranked list of documents as returned by a retrieval system, and (b) the qrel file that contains for each query the set of all documents judged as relevant or non-relevant.The results file has the form,
query-number Q0 document-id rank score Exp
where query-number is the number of the query, document-id is the external ID for the retrieved document, and score is the score that the retrieval system creates for that document against that query. Q0 (Q zero) and Exp are constants that are used by some evaluation software. You can download such a file for the READWARE retrieval system submitted to TREC 8 here.
The qrel file has the form,
query-number
0
document-id
relevance
where query-number is the number of the query, document-id is the external ID for the judged documents, 0 is a constant and relevance is the relevance assigned to the document for the particular query; relevance is either 0 (non-relevant) or 1 (relevant). You can download the qrel file for TREC 8 here.
For a given query, say query number 401, first calculate the total number of relevant documents, R, from the qrel file. Then read the results for the particular query from the input.READWARE file, find the corresponding documents for this particular query in the qrel file and the associated relevance score. Note that a document may appear more than once in the qrel file with different relevance score for different queries, so make sure you get the relevance score of the document associated with the correct query. Note also that if a returned document for a certain query in the input.READWARE file does not show up for the same query in the qrel file, then you can consider it as non-relevant and assign to it a relevance score of 0.
Compute the Average Precision of the ranked lists of documents returned by READWARE for each one of the 50 queries and the Mean Average Precision over all 50 queries. Submit the Average Precision values and the Mean Average Precision value you've calculated. Just so you can check the correctness of the output values, the Average Precision values for queries 401 and 402 are 0.0650 and 0.1704, respectively.
DO NOT SUBMIT YOUR CODE however proud of it you are :-)